Crediting Tofu and Soy Yogurt Products
November 29, 2023

Summary
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) released their second CACFP/SFSP guidance memo for 2024. The memorandum provides updated guidance on crediting tofu and soy yogurt products and supersedes a previous memo from 2016 (CACFP 21-2016). The memo extends the option of serving commercially prepared tofu and soy yogurt as meat alternates to infants 6-11 months participating in the CACFP. The memo also extends the ability to serve tofu and soy yogurt as meat alternates in SFSP.
Why It Matters
Offering a variety of foods and ingredients is a best practice in the CACFP. The ability to offer tofu and soy yogurt as meat alternates allows providers to further diversify their menus and better meet the dietary needs of vegetarians and culturally diverse groups.
Tofu
Tofu does not have a Federal standard of identity. For the School Meal Programs, CACFP, and SFSP, tofu must be commercially prepared and meet the following definition, established in 7 CFR 210.2 and 226.2 as “a soybean-derived food…basic ingredients [in tofu] are whole soybeans, one or more food-grade coagulants (typically a salt or an acid), and water.” Noncommercial tofu and soy products are not creditable. Through this memo, the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) is clarifying that this “tofu” definition also applies to SFSP.
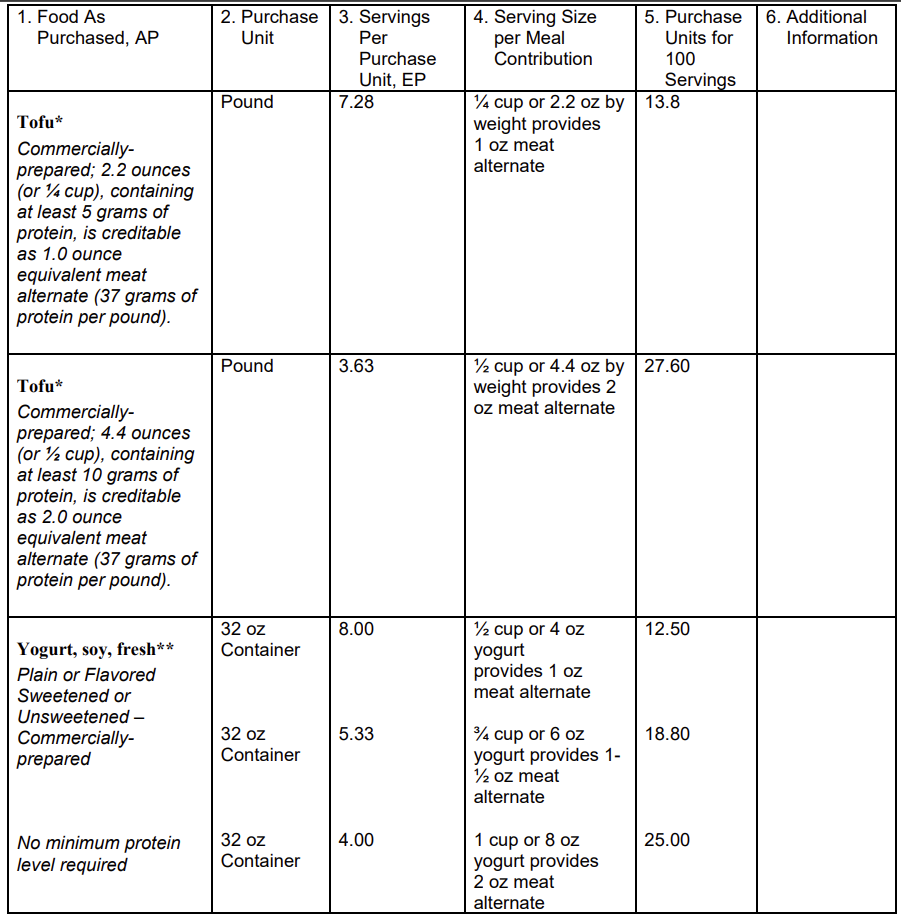
In the School Meal Programs, CACFP, and SFSP, 2.2 ounces by weight (ozw), or ¼ cup by volume, of commercially prepared tofu, containing at least 5 grams of protein, is creditable as 1.0 ounce equivalent of meat alternate. This is consistent with the DGAs’ recommended serving size for tofu and provides protein at levels similar to other CN-credited meat alternate foods. In the SFSP, the minimum serving amount for the meats/meat alternates component at lunch and supper is 2.0 ounce equivalents, which equals 4.4 ozw, or ½ cup by volume, of tofu, containing at least 10 grams of protein. At SFSP snack, when meats/meat alternates may be one of the two components offered, the minimum serving amount is 1.0 ounce equivalent, which equals 2.2 ozw, or ¼ cup by volume, of tofu containing at least 5 grams of protein. In the CACFP and NSLP infant meal patterns, the minimum serving amount of tofu for infants 6 through 11 months is 0- 4 tablespoons (¼ cup), or 2.2 ozw, of commercially prepared tofu, containing at least 5 grams of protein. Minimum serving sizes are listed as ranges for infants because not all infants are ready to eat solid foods at the same time. For all Child Nutrition Programs (CNP), if tofu contains greater than 5 grams of protein per 2.2 ozw, the tofu remains creditable as 1.0 ounce equivalent of meat alternate per 2.2 ozw (or ¼ cup volume) of tofu.
Soy Yogurt
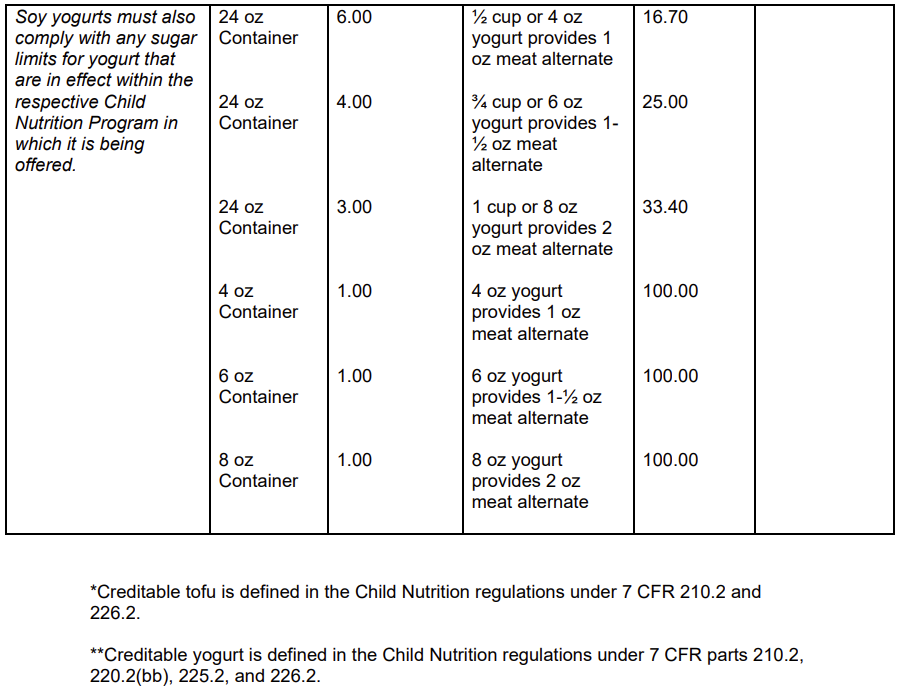
Additionally, ½ cup (or 4.0 ozw) of soy yogurt is creditable as 1.0 ounce equivalent of meat alternate. This is consistent with dairy yogurt crediting and allows schools, centers, day care homes, and summer meals sites to offer a non-dairy alternative to participants. In the CACFP and NSLP infant meal patterns, the serving size of soy yogurt is the same as for dairy yogurt, 0-4 ozw or ½ cup, for infants 6 through 11 months. Soy yogurt must also comply with any sugar limit for yogurt that is in effect within the respective CNP in which it is being offered.
Crediting Easily Recognizable Tofu and Tofu Products
Meals served through the School Meal Programs, CACFP, and SFSP are opportunities for children to learn how to build a healthy plate. Foods served should be easily recognized by children as part of a food group that contributes to a healthy meal. Tofu is widely recognized as a meat substitute, comes in a variety of textures (such as silken, soft, firm, and extra firm), and may be served many ways, including in culturally appropriate and traditional dishes. Firm or extra firm tofu, in stir-fries, omelets, miso soup and minced in lasagna as a ricotta cheese replacement, for example, may credit toward the meats/meat alternates component. Meat substitute products such as links and sausages made from tofu are also easily recognizable as meat substitutes and can be included as creditable items in a meal or snack if minimum protein requirements for the tofu ingredient are met.
However, tofu that is incorporated into items to add texture or improve nutrition, but is not easily recognizable as a meat substitute, such as in smoothies, sauces, and baked desserts, does not credit toward the meats/meat alternates component.
When considering commercially prepared tofu products as a meat alternate for a reimbursable meal or snack, such as tofu burgers or tofu sausages, the tofu ingredient must provide at least 5 grams of protein per 2.2 ozw, or ¼ cup, of tofu ingredient in order for the product to be creditable.
This information is not shown on a Nutrition Facts label. Therefore, the most appropriate way to ensure that the product meets the requirements outlined in this memorandum is to request that the product be manufactured under the Child Nutrition Labeling Program following a federally approved quality control program.
In circumstances where a Child Nutrition-labeled product is not available, Program operators can use a Product Formulation Statement (PFS) from the manufacturer to document how the product meets CNP requirements. For more information on Product Formulation Statements and Child Nutrition labels, please visit https://www.fns.usda.gov/cn/labeling/food-manufacturersindustry.
The following yield information can be used for purchasing and crediting: 1 pound of tofu with 37 grams of protein will have 7.28 quarter-cup servings per pound and provides 7.25 ounce equivalents of meat alternate.
Read the full guidance: Revised: Crediting Tofu and Soy Yogurt Products in the School Meal Programs, CACFP, and SFSP (CACFP 02-2024, SFSP 02-2024).
